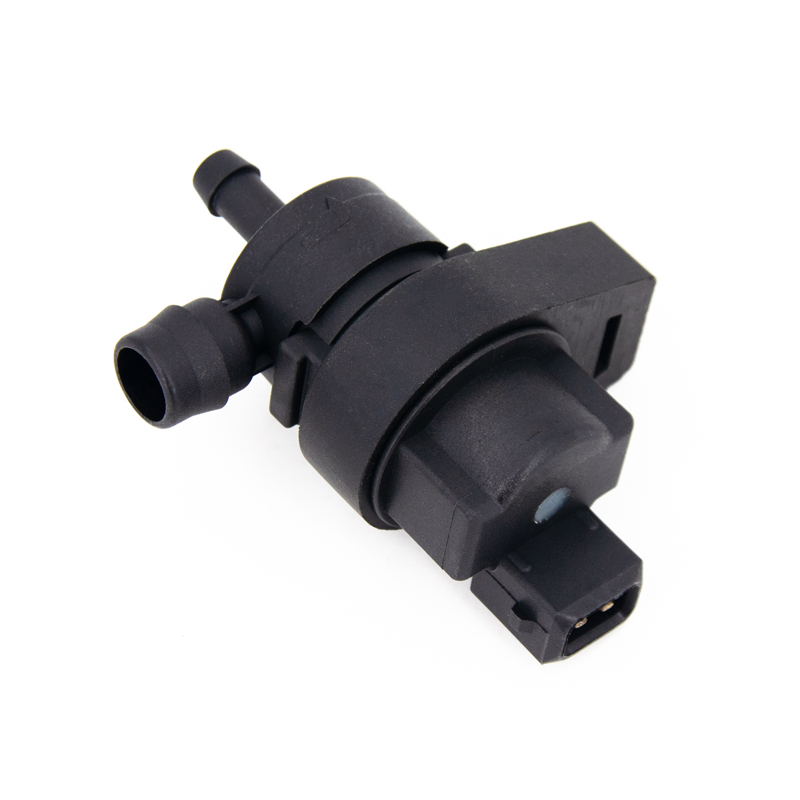
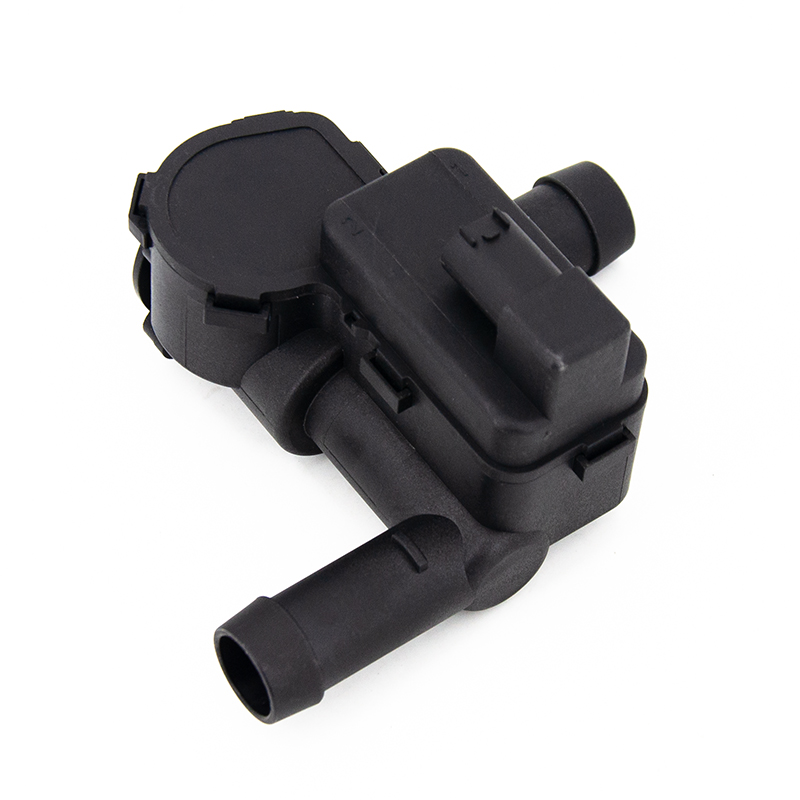
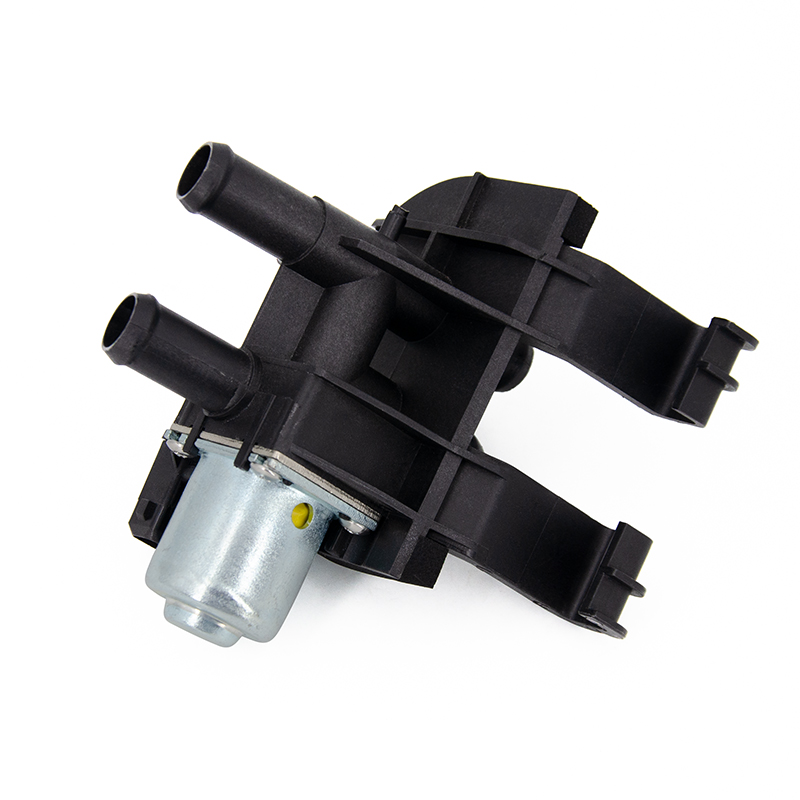
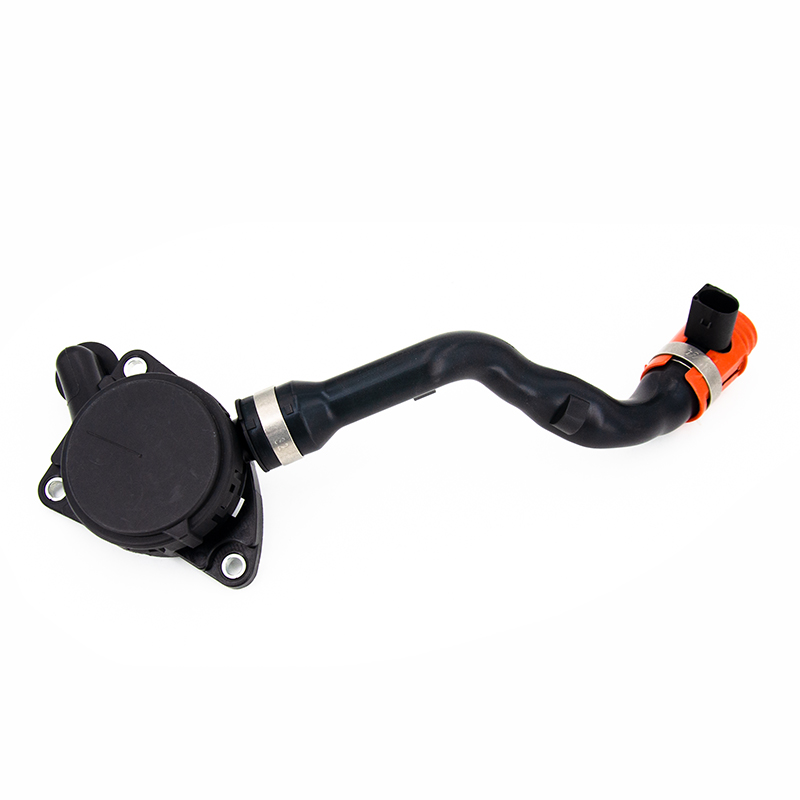
The thermostat is a valve that controls the flow path of the coolant. In the engine cooling system, the main function of the thermostat is to maintain the engine running within the ideal temperature range for high performance and high efficiency. When the engine is cold, the temperature of the coolant is usually low. At this time, the thermostat will close the passage of coolant to the radiator, which is achieved by the valve core or wax temperature sensing element inside the thermostat.
When the coolant temperature is low, the wax temperature sensing element inside the thermostat will remain solid, so the valve core is in a closed state. This closed state blocks the coolant flow path to the radiator, so that the coolant can only flow directly into the engine block or cylinder head water jacket through the inlet of the water pump. In this way, the coolant circulates inside the engine without passing through the radiator for heat dissipation, which helps the coolant to heat up quickly.
As the engine runs and the coolant temperature rises, the wax temperature sensing element inside the thermostat will gradually soften and expand. This expansion process will push the valve core to gradually open, allowing the coolant to flow to the radiator. Once the coolant temperature reaches or exceeds the temperature threshold set by the thermostat, the valve core will be fully opened and the coolant can circulate freely between the engine and the radiator to maintain the engine within the ideal temperature range.
Therefore, when the engine is too cold, the thermostat restricts the flow of coolant by closing the channel for coolant to flow to the radiator. This design ensures that the coolant circulates inside the engine and heats up quickly, thereby avoiding the performance degradation and efficiency loss of the engine due to low temperature.
If the thermostat fails or fails, it may cause the coolant to still flow to the radiator when the engine is too cold, or fail to open the channel in time to let the coolant dissipate heat when the engine is overheated. These situations may cause abnormal engine temperature, which in turn affects its performance and life.
Home / News / Industry News / How does the thermostat limit the flow of coolant when the engine is too cold?


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch