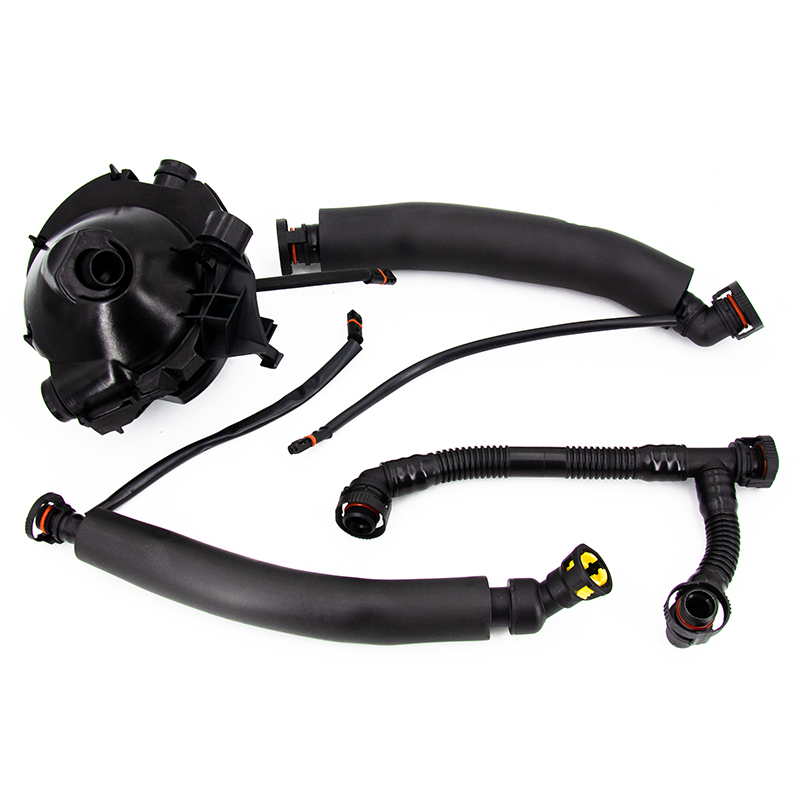
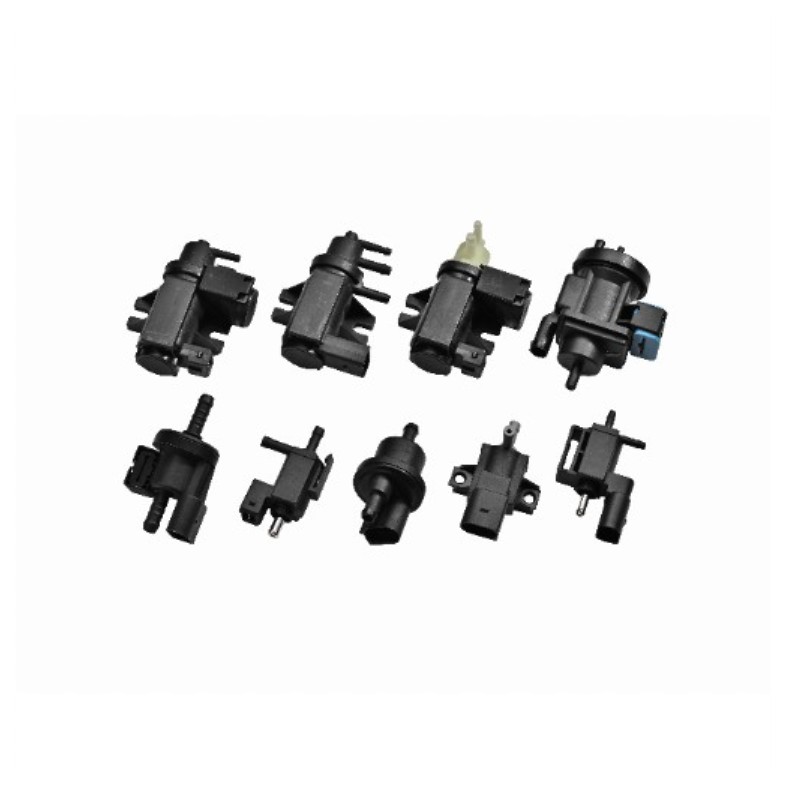
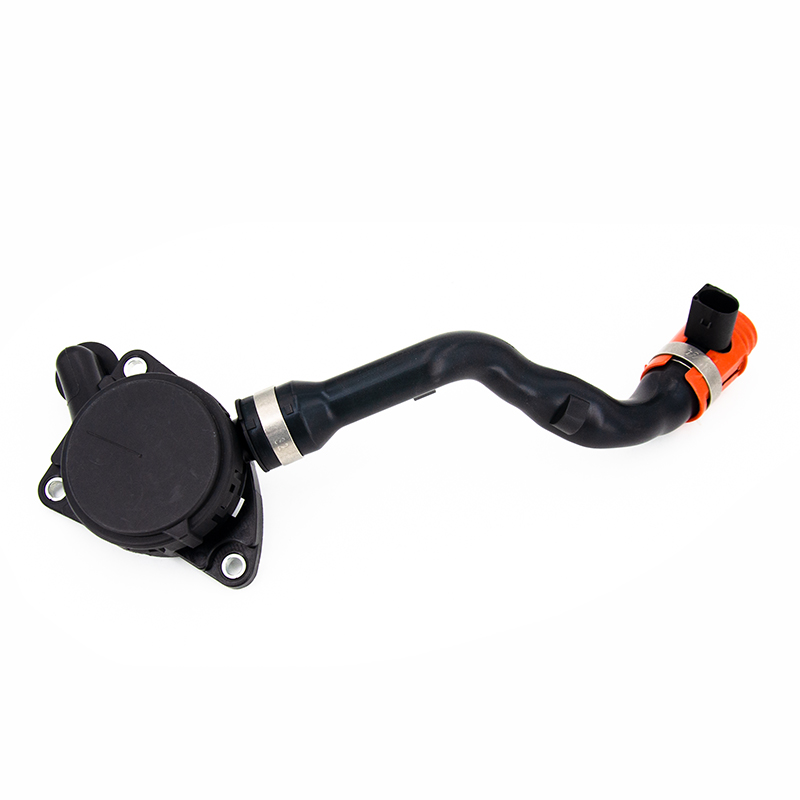
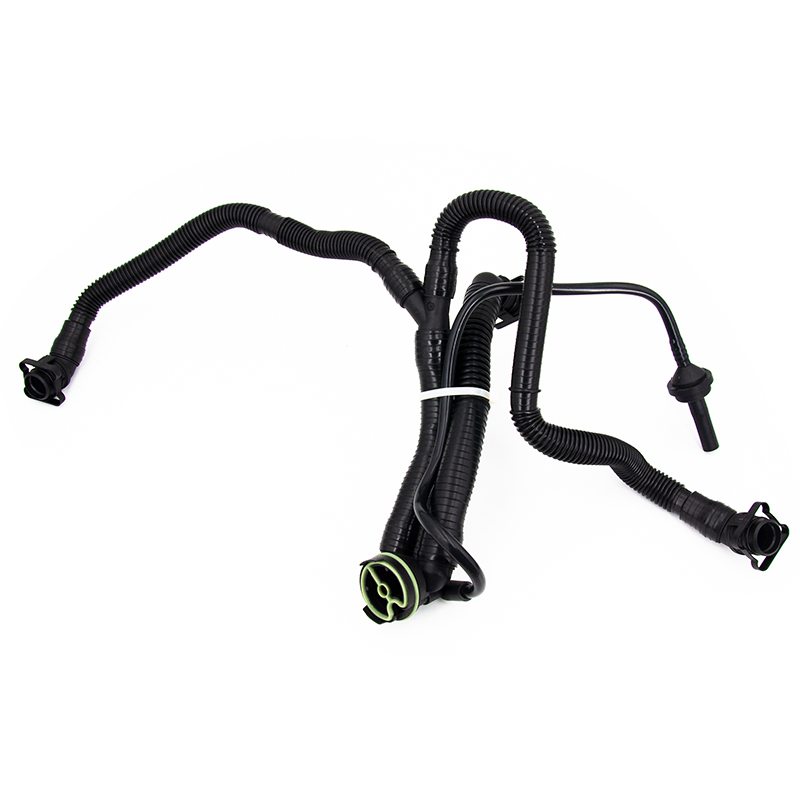
The main functions of the Crankcase breather hose include the following aspects:
Prevent lubricating oil from deteriorating and fuel dilution: By preventing the lubricating oil from being diluted by fuel, reduce the wear and corrosion of machine parts, and maintain the cleanliness of the lubricating oil.
Pressure reduction, temperature reduction and leakage prevention: Reduce the pressure and temperature in the crankcase, prevent the lubricating oil from leaking from the oil seal and gasket, and avoid the problem of temperature and pressure increase caused by gas leakage.
Recover combustible gas: The gas that has entered the crankcase is sucked into the cylinder again for combustion, CH compounds are recovered, and air pollution is reduced.
Regular maintenance of the PCV valve: Prevent pollutants from clogging the PCV valve, prevent polluted gas from flowing back into the air filter, reduce the filtering capacity, and ensure the normal operation of the engine.
Exhaust gas treatment during the combustion process of the mixture: At idle and low load, by controlling the flow section of the PCV valve, the mixture is prevented from being too lean and stable combustion is ensured; during acceleration and high load, the amount of blowby is increased to ensure that more exhaust gas is introduced into the cylinder for combustion.
The Crankcase breather hose (PCV hose) has a multi-faceted impact on the performance of the engine through its core component, the PCV valve. First, it helps maintain the pressure balance in the crankcase and prevents seal damage caused by excessive or low pressure, thereby ensuring the stability of the engine's internal structure.
At idle or low load, the PCV valve will open to the maximum, allowing only a small amount of gas to pass through to avoid too lean a mixture and ensure stable combustion; at high speed or high load, the valve will open halfway to increase the flow rate, increase the amount of blowby, and ensure the normal operation of the engine during acceleration.
In addition, by recovering the combustible gas in the crankcase and reintroducing it into the intake manifold for combustion, it not only helps reduce harmful emissions, but also improves fuel economy. At the same time, the system can also effectively prevent oil deterioration and fuel dilution, reduce wear and corrosion of mechanical parts, and extend the service life of the engine.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch