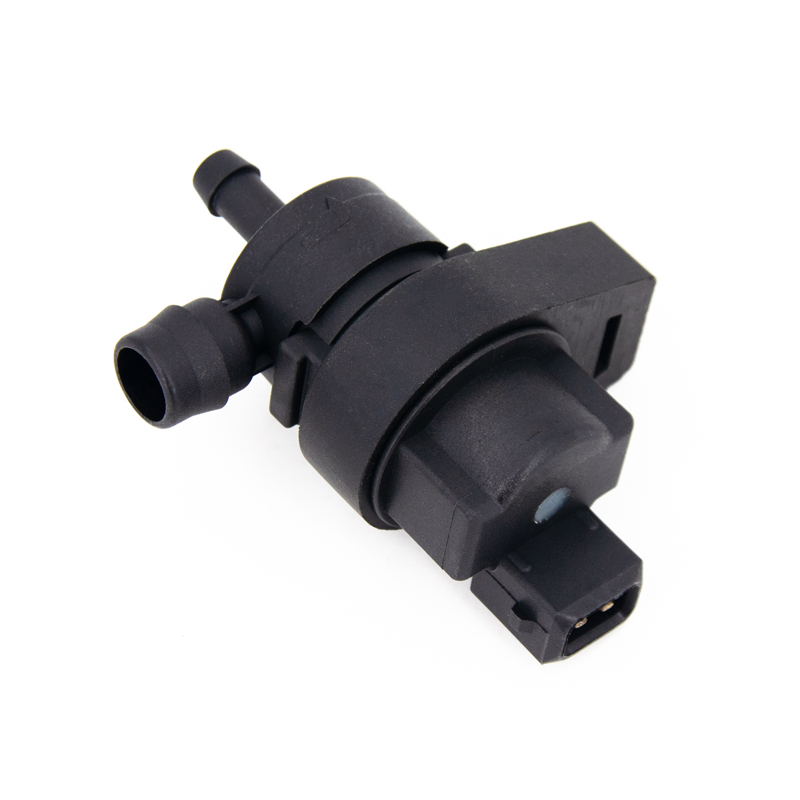
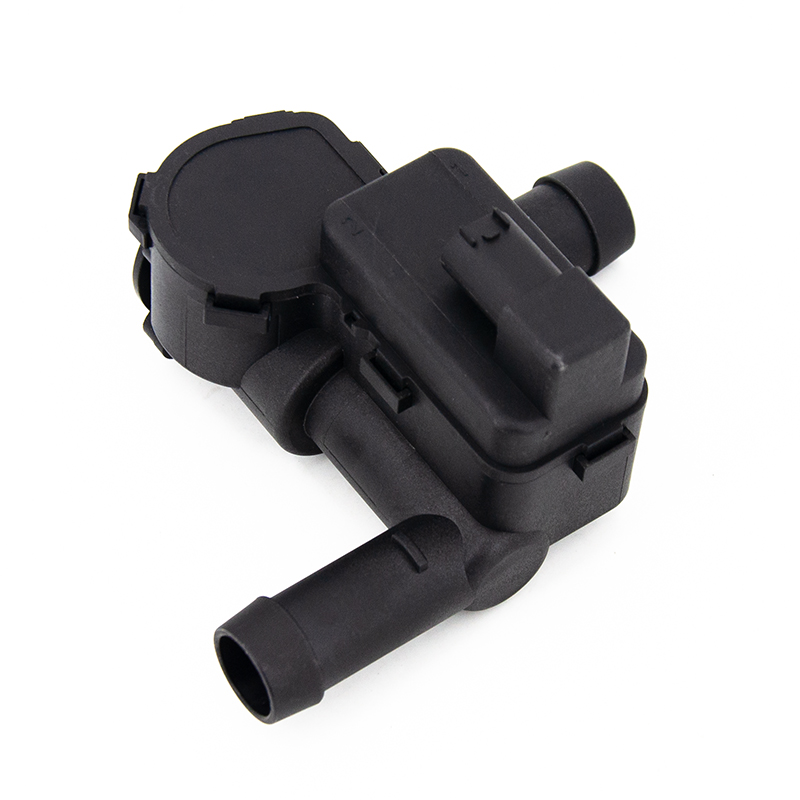
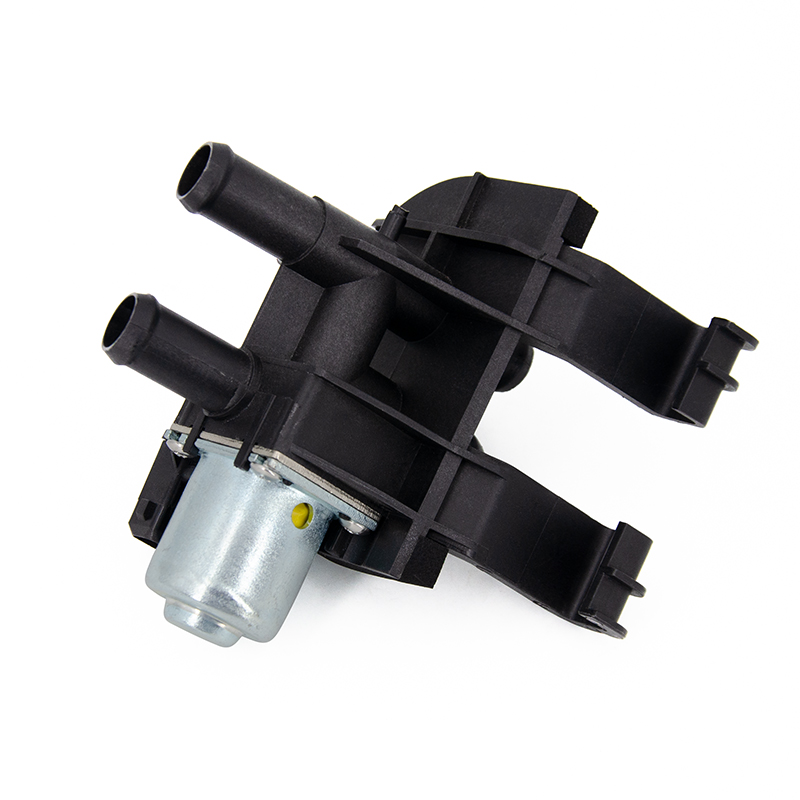
If the Auxiliary Cooling Water Pump fails, the engine cooling system will not work properly, which will cause a series of serious problems. The main function of the auxiliary water pump is to increase the coolant circulation pressure and ensure that the coolant can effectively flow through key parts such as the engine cylinder block and radiator. If the water pump fails, the coolant flow slows down or even stagnates, resulting in the inability to dissipate heat in time, and the engine temperature rises rapidly, which may trigger a high temperature alarm, and even cause the engine coolant to boil in severe cases.
High temperature will cause the engine ECU to enter protection mode and actively reduce power output (such as turbocharged models may limit boost pressure) to prevent further damage. Problems such as weak acceleration, unstable idle speed, and increased fuel consumption may occur.
High temperature may cause uneven thermal expansion of the aluminum alloy cylinder head, causing deformation, which in turn causes the cylinder gasket to burn and cause the coolant to mix with the engine oil. High temperature deteriorates the lubrication between the piston ring and the cylinder wall, which may cause cylinder pull (abnormal wear of the piston and the cylinder wall). Turbocharged models rely on coolant circulation to dissipate heat, and water pump failure may cause high-temperature sintering of the turbine shaft.
High temperature reduces the viscosity of the engine oil, weakens the lubrication ability, and aggravates the internal wear of the engine. High temperature may damage precision components such as oxygen sensors and knock sensors. Stagnant coolant may partially vaporize, causing a sudden increase in pipeline pressure, and even causing water pipe bursts or water tank leaks. If it is operated in an overheated state for a long time, it may cause irreversible damage such as piston welding and crankshaft locking, which will eventually lead to engine overhaul or scrapping.
During use, regularly check the coolant level and water pump operation (such as belt-driven water pumps, check the tension). Replace the coolant according to the manufacturer's recommendations to avoid corrosion of the internal structure of the water pump. If the water temperature is abnormal, stop the car for inspection immediately to avoid forced driving.
Home / News / Industry News / What impact may it have on the engine if the Auxiliary Cooling Water Pump fails?


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch