An auxiliary cooling water pump is an electric drive device used in the cooling system of an automobile. Its main function is to provide additional flow pressure for the coolant to ensure smooth circulation of the coolant in the engine cooling system.
1. Working principle
The auxiliary water pump is usually driven by a small electric motor. It sucks the coolant from the water pump inlet by rotating the impeller, and discharges it from the outlet after pressurization, pushing the coolant to flow in the engine cooling system. It is usually installed in the bypass line of the engine cooling system and works in parallel with the main water pump, but does not depend on the operation of the engine.
2. Main function
Increase the coolant flow pressure: In some cases, especially in turbocharged engines or high-performance engines, the cooling demand is high, and the auxiliary water pump can provide additional coolant flow to ensure heat dissipation efficiency.
Achieve more precise temperature control: Through electric control, precise control of coolant flow can be achieved, such as automatic opening or closing when the engine is started, after the engine is turned off, or under specific working conditions (such as cold start, heating demand).
Extending engine life: A more efficient cooling system can reduce the risk of engine overheating, thereby extending the service life of the engine.
3. Application scenarios
Turbocharged engines: Turbochargers generate a lot of heat when running at high speeds. Auxiliary water pumps can ensure that the turbochargers are still fully cooled after the engine is turned off.
Hybrid and electric vehicles: In electric vehicles, batteries and electric motors need to be continuously cooled. Auxiliary water pumps can provide a stable coolant circulation for these components.
Luxury or high-performance models: In order to improve driving comfort and engine performance, some high-end models will be equipped with auxiliary water pumps for more precise temperature control.
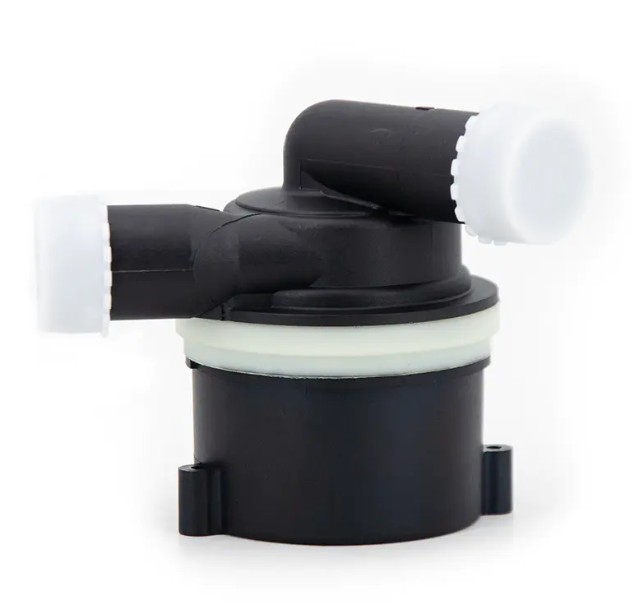

What is the difference between a water pump and an auxiliary water pump?
Although both are part of the cooling system, they have obvious differences in driving mode, working principle, application scenario and function.
1. Traditional water pump (mechanical water pump)
Drive mode: Driven by the engine crankshaft through a belt, it is a mechanical drive.
Working principle: When the engine is running, the belt drives the water pump impeller to rotate, pushing the coolant to circulate in the engine cooling system.
Function: Mainly responsible for the cooling of the engine body, it is the core component of the cooling system.
Features:
Depends on the engine to run. Once the engine is turned off, the water pump stops working.
Usually there is only one water outlet, and the coolant can only flow in one direction.
It cannot continue to provide cooling for components such as turbochargers after the engine is turned off.
2. Auxiliary water pump (electric water pump)
Drive mode: driven by an independent motor, not dependent on the engine operation.
Working principle: The motor drives the impeller to rotate, and the coolant is pressurized and sent into the cooling system, which can achieve two-way or one-way flow.
Function: Mainly used for turbochargers, batteries, motors and other components that require continuous cooling, and can also be used for cooling after the engine is turned off.
Features:
It can continue to work after the engine is turned off, suitable for turbocharged engines.
Usually has intelligent control function, which can automatically start and stop according to temperature, vehicle speed and other conditions.
Small size, low noise, suitable for the compact design of modern cars.
| Project | Conventional water pump | Auxiliary water pump |
| Drive mode | Mechanical drive (belt) | Electric drive |
| Is it engine-dependent? | Yes | No |
| Can it work after the engine is turned off? | No | Yes |
| Can it be intelligently controlled? | No | Yes |
| Main purpose | Engine block cooling | Turbocharger, battery, electric motor, etc. |
| Installation location | Engine front | Usually in bypass line |
When and how to install the auxiliary electric water pump?
When to install the auxiliary electric water pump?
The installation of an auxiliary electric water pump is usually carried out in the following situations:
Turbocharged engine: The turbocharger still needs to be cooled after the engine is turned off, and traditional water pumps cannot meet this requirement.
Hybrid and electric vehicles: The battery and electric motor need to be continuously cooled, and the auxiliary water pump can provide a stable coolant circulation.
High-performance engine: In order to improve engine performance and reliability, some high-performance models will be equipped with an auxiliary water pump.
Luxury model: In order to improve driving comfort and engine life, some luxury models will use an auxiliary water pump system.
How to install an auxiliary electric water pump?
The installation of an auxiliary electric water pump usually requires the following steps:
(1) Preparation
Make sure that the engine cooling system has been completely cooled to avoid burns.
Prepare all necessary tools and parts, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, coolant, sealing tape, etc.
Check the vehicle manual or consult a professional technician to confirm whether it is suitable to install the auxiliary water pump.
(2) Installation location
Common installation location: Usually installed in the bypass line of the engine cooling system, in parallel with the main water pump.
Installation method: Install the water pump in the coolant pipeline, ensure the correct inlet and outlet direction to avoid reverse flow.
(3) Connect the power supply
The auxiliary water pump is usually powered by the vehicle's 12V or 24V power supply and needs to be connected to the vehicle's electronic control system.
A relay or control module needs to be installed to achieve intelligent control of the water pump (such as automatic start and stop based on temperature, vehicle speed and other conditions).
(4) Connect the coolant pipeline
Use a suitable hose or hard pipe to connect the inlet and outlet of the water pump to other components of the cooling system.
Ensure that the connection is well sealed to prevent leakage.
During installation, be careful to avoid air entering the system to prevent "cavitation".
(5) Testing and debugging
After installation, start the engine and check whether the water pump is working properly.
Check whether the coolant flows smoothly and whether there is any abnormal sound or leakage.
Use a temperature sensor to monitor the engine temperature to ensure that the cooling system is working properly.
| Project | Contents |
| Auxiliary cooling water pump | An electrically driven cooling water pump used to increase the coolant flow pressure to ensure that the engine and other components operate at the appropriate temperature. |
| Difference between water pump and auxiliary water pump | Traditional water pumps rely on the engine to operate, while auxiliary water pumps operate independently and are suitable for special needs such as turbocharging and electric. |
| When to install auxiliary water pump | Applicable to turbocharged engines, hybrid vehicles, high-performance vehicles, etc. to achieve more efficient cooling and longer service life. |
| How to install auxiliary water pump | Usually installed in the bypass line, connected to the power supply and coolant pipeline, it needs to be tested and debugged to ensure the normal operation of the system. |


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch