Content
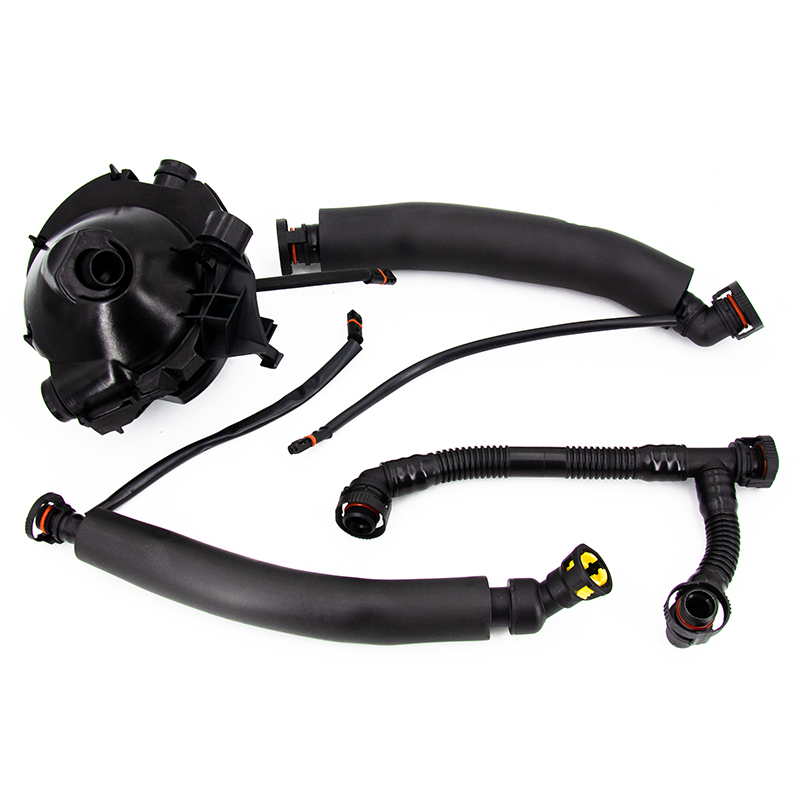
Position of the PCV hose in the engine system
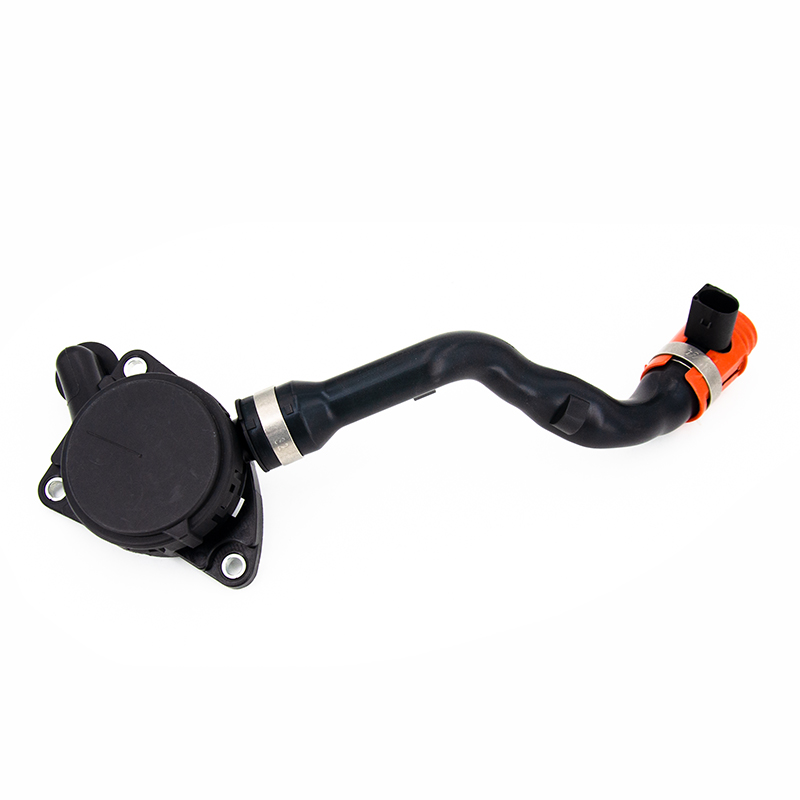
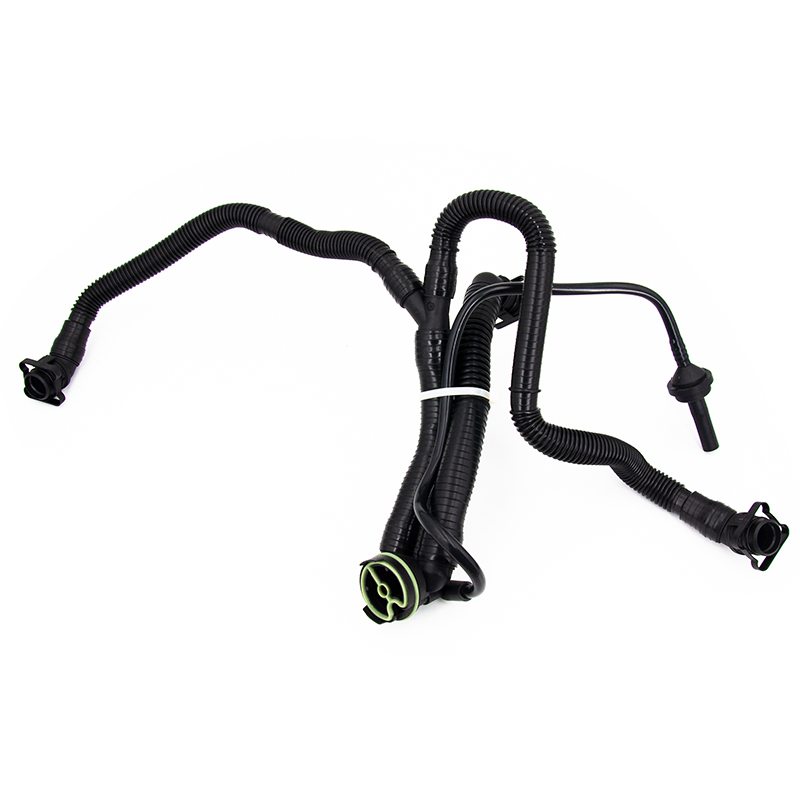
The PCV hose usually connects the following components: crankcase, PCV valve (crankcase ventilation valve), intake manifold, throttle body, and air filtration system, forming a complete closed-loop structure of the positive crankcase ventilation system (PCV system).
Core function analysis of the PCV hose
Exhaust gas recovery and reburning: During engine operation, a large amount of exhaust gas (oil–gas mixed gas) is generated in the crankcase. The PCV hose guides these gases into the intake system for reburning, reducing pollutant emissions.
Crankcase pressure balancing: Through a stable exhaust channel, it prevents excessive internal crankcase pressure, preventing oil seal leakage, gasket aging, oil overflow, and controlling oil consumption.
Oil–gas separation: In cooperation with the PCV valve, it reduces engine oil being drawn into the combustion chamber with exhaust gas and lowers abnormal oil consumption.
Maintaining stable engine operation: Stabilizing crankcase air pressure → stabilizing the intake system → stabilizing the combustion state → improving engine running smoothness.

Importance of the PCV hose to the emission system
The PCV system is part of the emission control system: reducing HC (hydrocarbon) emissions, meeting emission regulation requirements, and lowering exhaust pollutant concentrations. Abnormal PCV hoses will directly lead to excessive emission problems.
Common fault manifestations include hose aging and cracking, hose hardening, joint air leakage, negative pressure leakage, and abnormal air intake in the intake system.
Typical symptoms: unstable idle, increased fuel consumption, power decline, warning light on, abnormal emissions, abnormal oil consumption.
Materials and performance indicators of PCV hoses
Common materials: Oil-resistant rubber, EPDM composite rubber, high-temperature resistant silicone hoses, fluororubber composite hoses.
Key performance indicators: high-temperature resistance (≥120 °C), oil resistance, anti-aging performance, resistance to vacuum deformation, corrosion resistance.
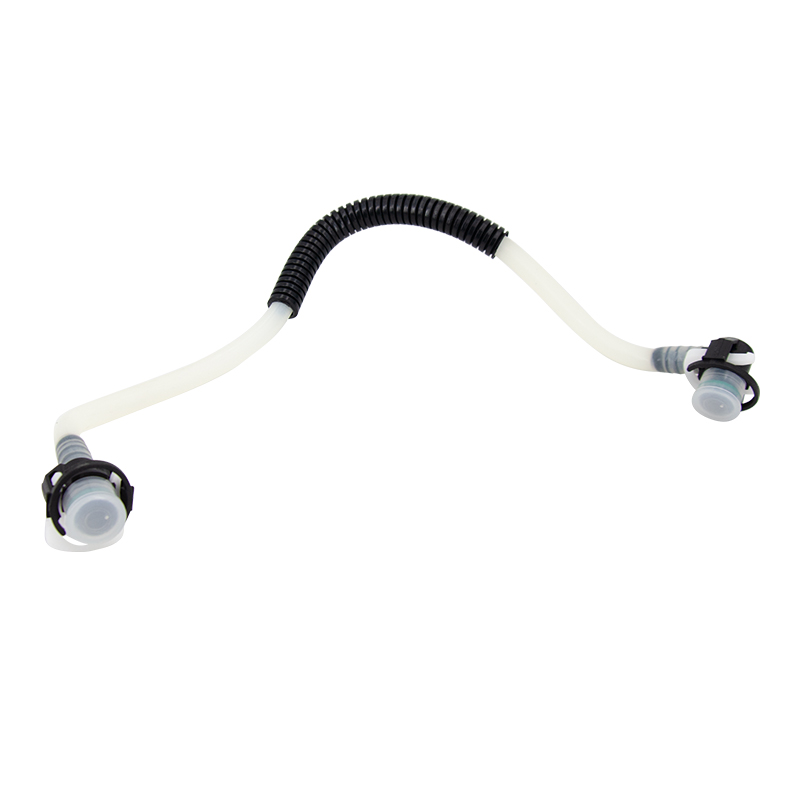
Difference between PCV hoses and ordinary rubber hoses
| Comparison item | PCV hose | Ordinary rubber hose |
| Oil resistance | Strong | Average |
| High-temperature resistance | Strong | Average |
| Resistance to negative pressure | Strong | Weak |
| Emission adaptation | Dedicated | Non-dedicated |
| Service life | Long | Short |
Recommended replacement cycle: service life ≥ 3–5 years, replace when aging and cracking are found, hardening and loss of elasticity, air leakage, abnormal engine operating conditions, and during synchronous inspection of PCV valve replacement.
Practical selection suggestions: choose oil-resistant and high-temperature-resistant materials, match vehicle interface specifications, select original factory specifications or equivalent parts, focus on sealing performance, and ensure vacuum-resistant structural design.
Conclusion
The PCV hose is not only a connecting pipeline, but also an important component of the engine emission system and internal pressure control system. It plays a key role in exhaust gas recovery, pressure balancing, oil–gas separation, emission control, and stable engine operation. A well-maintained PCV hose ensures more stable engine conditions, lower fuel consumption, and a healthier emission system, making it a critical component that should not be overlooked.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch