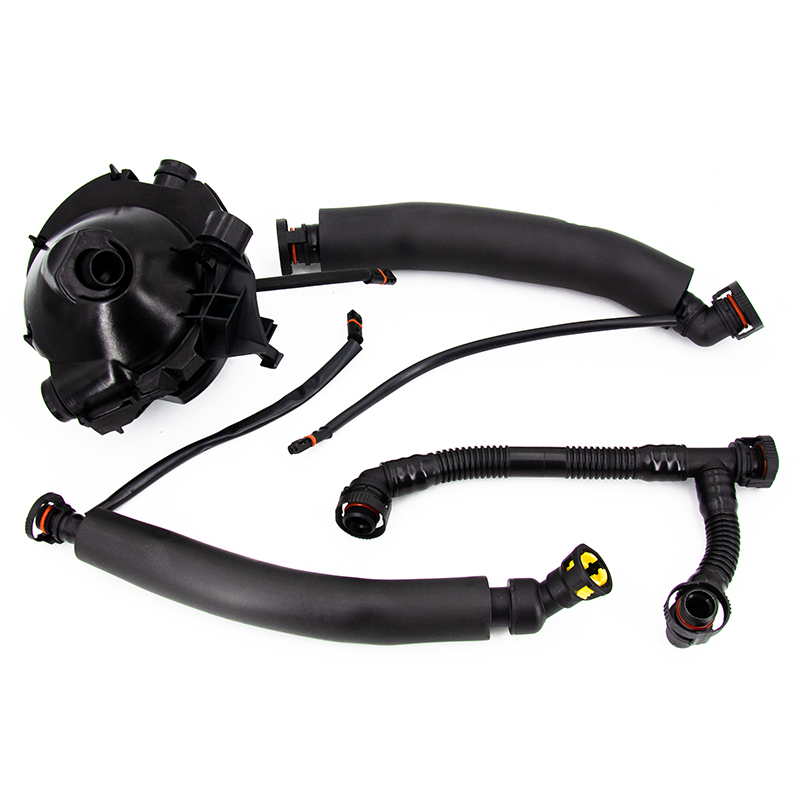
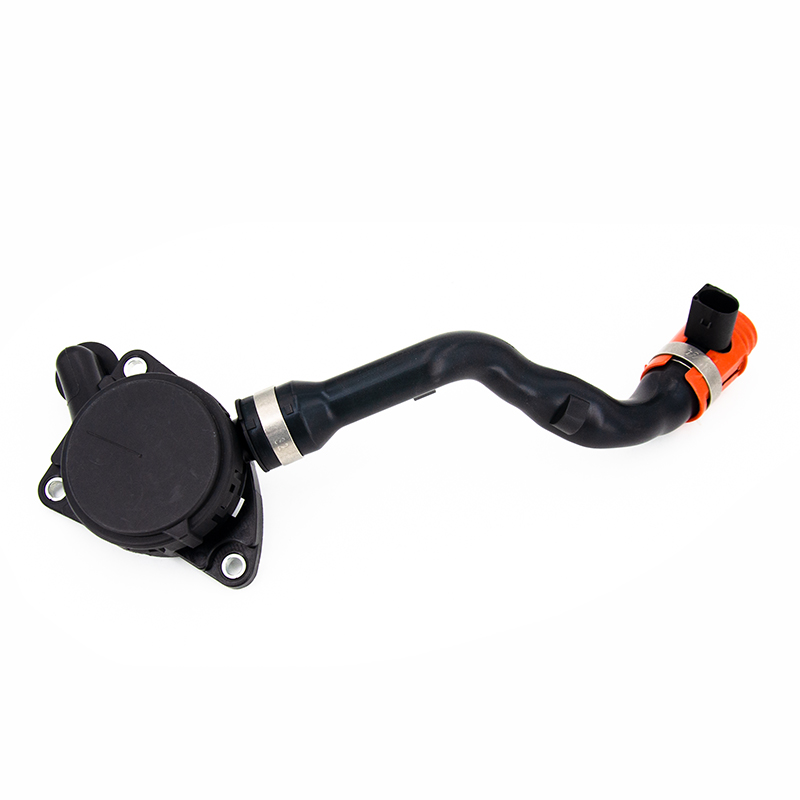
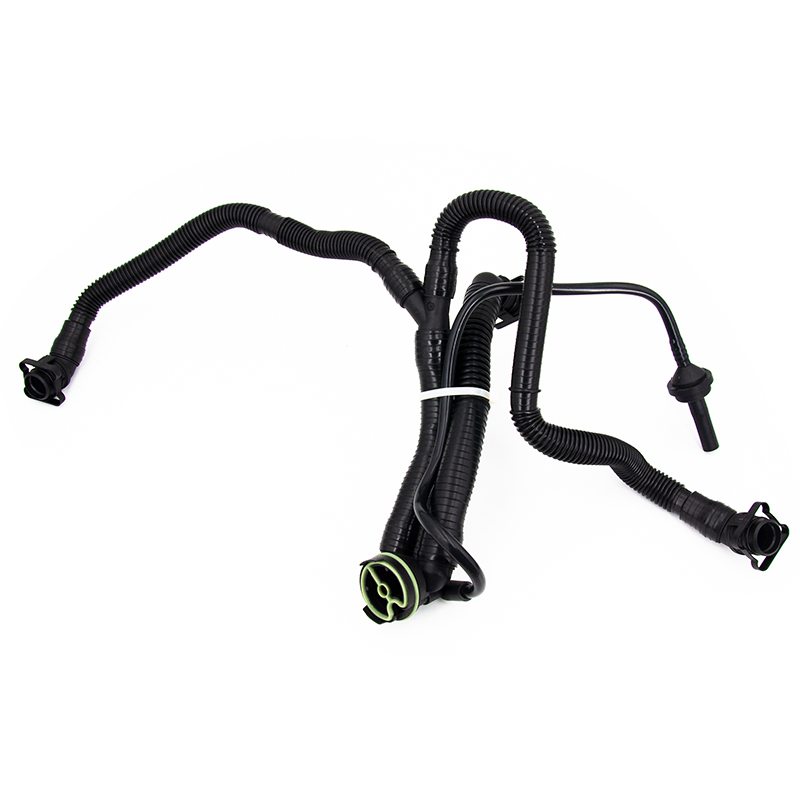
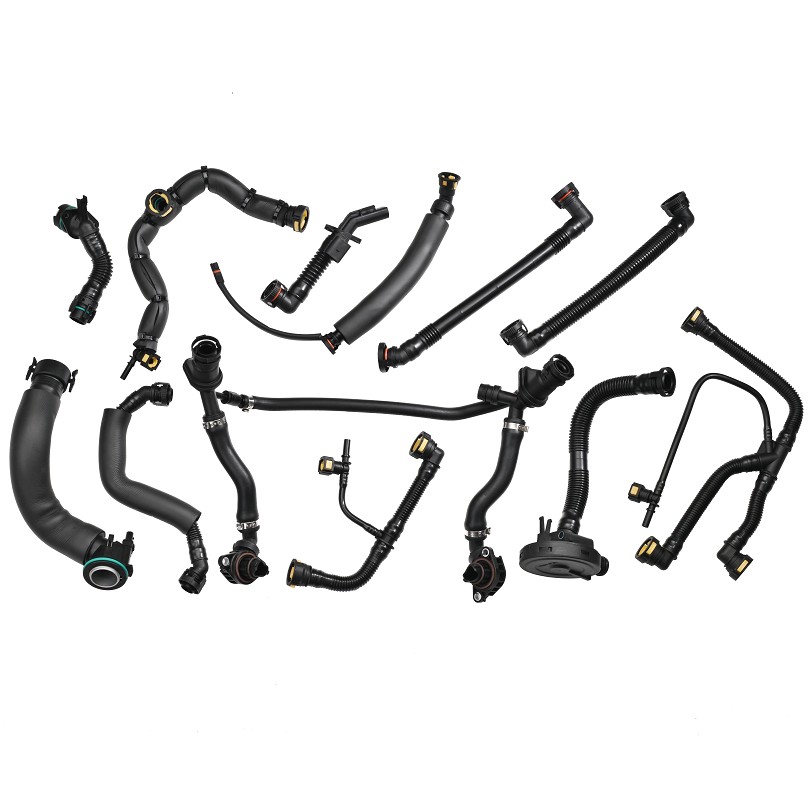
Coolant flange failure is typically caused by a combination of factors, including high-temperature fatigue, seal aging, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress. As a critical connection point in the cooling system, cracks or deformation in the coolant flange can directly lead to coolant leakage, resulting in engine overheating and even serious mechanical failure.
Content
What is a Coolant Flange?
Coolant flanges are typically used to connect different components of the cooling system. Their main function is to allow the coolant to flow smoothly through the system and ensure a good seal between components to prevent coolant leakage.
These flanges are usually located on the engine block or radiator, connecting the cooling system's pipes, coolant pump, radiator, and other core components. This tight connection allows the coolant to circulate throughout the system, absorbing and dissipating heat, thereby maintaining the engine within a suitable operating temperature range.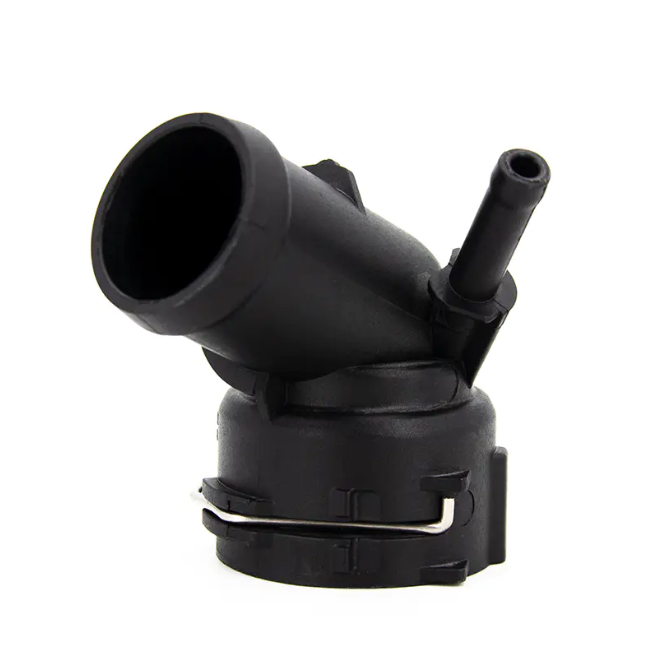
Main Causes of Coolant Flange Failure
The design and quality of the coolant flange are crucial to the performance of the cooling system. However, during long-term operation, the following factors often cause its failure:
1. Long-term High Temperatures and Thermal Cycling
Coolant flanges are subjected to extreme operating environments for extended periods. 1. Repeated engine starting and stopping cause frequent thermal expansion and contraction of the flange. Over time, this thermal stress can make the plastic flange brittle, eventually leading to micro-cracks.
2. Aging of O-rings
The flange connection to the engine block typically relies on rubber O-rings to prevent leaks. Due to the chemical composition of the coolant and continuous high temperatures, the O-rings gradually harden, lose elasticity, or degrade, causing leaks at the coolant flange connection.
3. Electrochemical Corrosion and Coolant Quality
If the coolant in the cooling system is not changed for a long time, or if inferior coolant is used, its internal chemical balance will be disrupted. Acidic substances or electrochemical reactions can corrode metal flanges or weaken the structural strength of plastic flanges.
4. Physical Damage and Over-tightening
During maintenance, excessive torque on the mounting bolts can cause deformation or even cracking of the coolant flange base. Furthermore, severe vibrations during engine operation can also loosen the connection.
Performance Standards for High-Quality Coolant Flanges
To ensure the long-term reliability of the cooling system, high-performance coolant flanges must possess the following characteristics:
Superior Sealing: Precision machining ensures effective prevention of coolant leakage even under high pressure.
High Temperature and Pressure Resistance: Utilizing high-strength composite materials or corrosion-resistant alloys, capable of withstanding extreme pressures during the cooling cycle.
Dimensional Accuracy: Perfectly matched with original equipment piping and pump body, reducing installation stress.
Although a seemingly insignificant component, the coolant flange plays a crucial role in maintaining engine thermal balance. Regularly inspecting the flange's condition and promptly replacing worn parts are essential measures to prevent vehicle overheating and protect the engine.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch